Next: Self-Consistent Field Theory Up: Spatial Inhomogeneity. Interfaces Previous: Spatial Inhomogeneity. Interfaces
![]()
![]()
![]()
Next: Self-Consistent Field Theory
Up: Spatial Inhomogeneity. Interfaces
Previous: Spatial Inhomogeneity. Interfaces
The simplest description of liquid-gas interface: a sharp transition
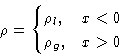
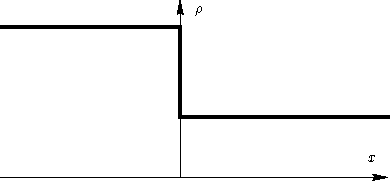
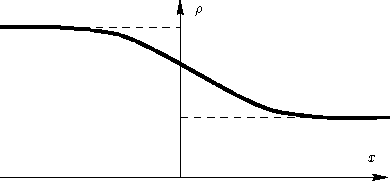
Problems: