


Next: Phase Transitions of Ising
Up: Ising Model and Its
Previous: Ising Model and Its
Subsections
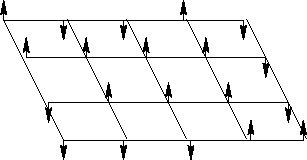
We have N spins 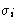 , i=1, 2,... on a lattice with
coordinate number z. Each spin can be either up or
down
, i=1, 2,... on a lattice with
coordinate number z. Each spin can be either up or
down![[*]](/icons/foot_motif.gif) :
:
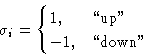
- 1.
- Each spin interacts with external field H:
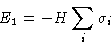
- 2.
- Each pair of neighbors interacts:
- (a)
- Parallel spins are favored--energy -J, J>0
- (b)
- Antiparallel spins are discouraged--energy +J
This can be written as 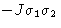 . The total interaction:
. The total interaction:
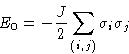
Here (i,j) means sum over all pairs of nearest neighbors
Result:
| 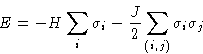 |
(1) |
Microscopic state of the system--combination of all spins:
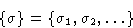
Partition function:
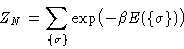
We don't have momenta here--this is actually a configuration
integral rather than partition function!
Free energy:
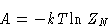
Average magnetization (H is conjugated to 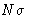 !)
!)
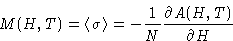
Susceptibility:
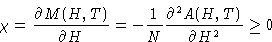
Energy:
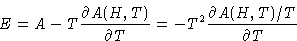
Specific heat:
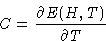
© 1997
Boris Veytsman
and Michael Kotelyanskii
Mon Oct 13 22:07:20 EDT 1997
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() , i=1, 2,... on a lattice with
coordinate number z. Each spin can be either up or
down
, i=1, 2,... on a lattice with
coordinate number z. Each spin can be either up or
down![]() :
:
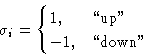

![]()
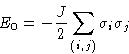
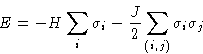
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() !)
!)
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()