Next: Applications of Ising Model Up: Ising Model and Its Previous: Model
![]()
![]()
![]()
Next: Applications of Ising Model
Up: Ising Model and Its
Previous: Model
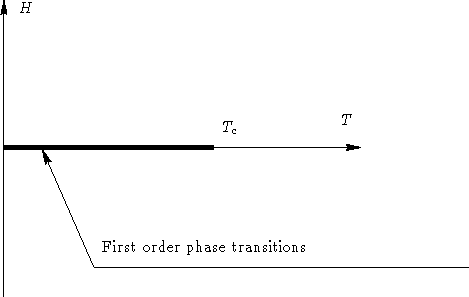
Let H=0 (symmetric case). Entropy wants spins to be disoriented, energy--to be parallel
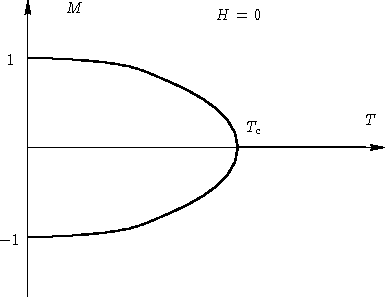
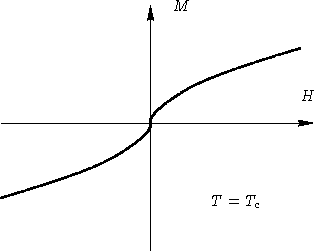
If ![]() , magnetization M is parallel to H. There is a function
M(H,T). What happens at
, magnetization M is parallel to H. There is a function
M(H,T). What happens at ![]() ?
?
![]()
![]()
![]()
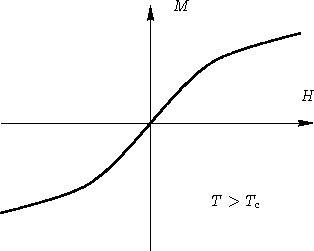
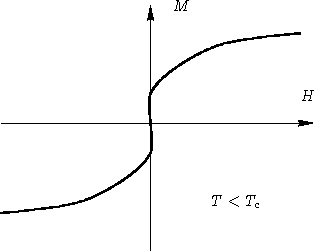
In critical point susceptibility is infinity!
Since amplitude of fluctuations is
![]()