Next: Quiz Up: Molecular Dynamics I Previous: Numerical Integration. Finite Difference
![]()
![]()
![]()
Next: Quiz
Up: Molecular Dynamics I
Previous: Numerical Integration. Finite Difference
Before we proceed developing program for the MD simulations of
particles
interacting via the Lennard-Jones (or any other) potential
we have to derive the expression for the force, and
for the characteristic time scale, to determine the
integration time step ![]() .
.
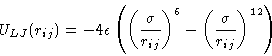 |
(9) |
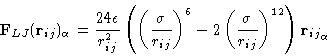 |
(10) |
The time scale can be determined by calculating the characteristic
oscillations frequency for two particles interacting
via the Lennard-Jones potential. Consider two particles
of the same mass that are bound together by the Lennard-Jones potential
with parameters ![]() and
and ![]() . Distance
between them is close to the equilibrium distance
. Distance
between them is close to the equilibrium distance ![]() .As the force is central we can consider a one-dimensional problem
.As the force is central we can consider a one-dimensional problem
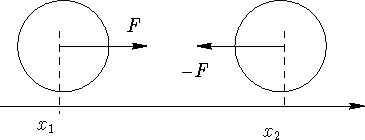
If we assume, that they oscillate around the rij0
with a very small amplitude, we can expand the potential energy around rij0
and find for the force:
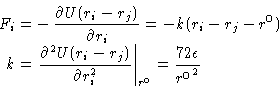 |
(11) |
Equations of motion and characteristic frequency then are:
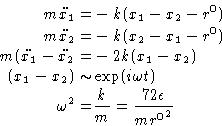
This introduces the error in the numerical integration and energy conservation. The cure is to use spline, that would make the potential and force continuous. This, however precludes the cut-off correction or makes it difficult. Simple way to cope with it is just to ignore the error in the force if the rc is large enough, and to use the shifted potential energy U = U - U(rc) to control the energy conservation.
© 1997 Boris Veytsman and Michael Kotelyanskii