


Next: Van der Waals Equation
Up: Imperfect Gases and Liquids.
Previous: Interaction Energy
Subsections
For ideal gas U=0. Let us discuss slightly non-ideal gas,
and expand 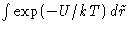 when
when 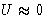 .
.
- Simple idea:
- Expand
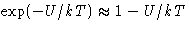
- Problem:
- Since
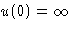 , this never works!
, this never works!
- Solution:
- Let us discuss Mayer function instead:
| 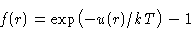 |
(3) |
When 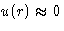 Mayer function is small. When
Mayer function is small. When 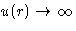 we
have
we
have 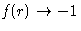 .
. - Assumption:
- For slightly non-ideal gas Mayer function is small
on average:
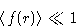
Gibbs factor:
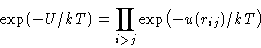
Express through Mayer function:
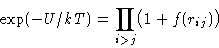
Expand:
| 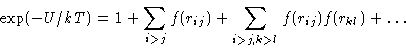 |
(4) |
When is f(r) is non-zero? For hard spheres--when
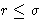 . This is collision. Low density gas--not many
collisions! Take a volume V, where collisions are rare. It means
neglecting products of f-functions.
. This is collision. Low density gas--not many
collisions! Take a volume V, where collisions are rare. It means
neglecting products of f-functions.
To obtain ZN, integrate (4) over
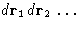
- 1.
- First term:
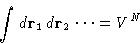
- 2.
- Second term: a collection of equal contributions like
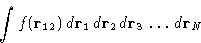
Number of terms: 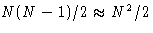
- (a)
- Integration over
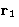 --factor V
--factor V
- (b)
- Integration over
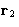 --factor
--factor 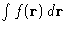
- (c)
- Integration over
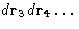 --factor VN-2
--factor VN-2
Result:
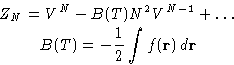
B(T) is second virial coefficient
Taking log:
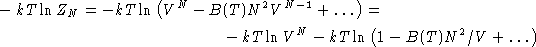
Since 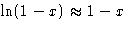 , we obtained:
, we obtained:
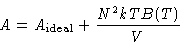
Pressure:
| 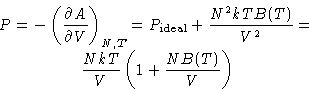 |
(5) |
If we know u(r), we can calculate B!
- Dimension:
- Since f(r) is dimensionless, B has dimension of
volume.
- Model:
- Hard core plus attraction, equation (2).
- High Temperatures:
- If
 , Mayer function is
, Mayer function is
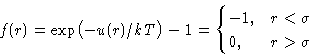
and
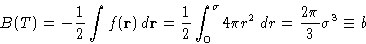
This is four times the volume of one molecule
At high temperatures B(T)=b describes the hard core
volume of gas.
- Lower Temperatures:
- Integrate from to
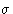 and from
and from
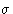 to
to 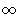 . First integral gives b, second is
. First integral gives b, second is
![\begin{displaymath}
\frac12\int_{\sigma}^{\infty}\Big[1-\exp\big(-u(r)/kT\big)\Big]4\pi r^2\,dr
\end{displaymath}](img62.gif)
Expansion:
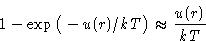
and
| 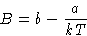 |
(6) |
with positive a (at 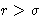 potential u is attractive!)
potential u is attractive!)
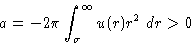
- Assumption:
- We assume (6) is valid for all temperatures.
- Meaning of the coefficients:
- b describes steric repulsion,
a describes long range attraction.
- Behavior of B(T):
-
- At high T we have B(T)>0 (repulsion)
- At lower T we have B(T)<0 (attraction)
- At some temperature Tb it is zero B(Tb)=0. This is
Boyle point of gas.
If we include the terms fikflm in expansion ZN, we will
obtain:
| 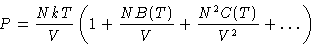 |
(7) |
C(T) is the third virial coefficient. Similarly fourth, fifth....
We can compute any virial coefficient if we know u(r)!
Will these series converge? Yes, if
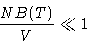
It means that distances between molecules  their sizes!
their sizes!
This is true for gases, but not for liquids!
Virial expansion does not work for liquids.



Next: Van der Waals Equation
Up: Imperfect Gases and Liquids.
Previous: Interaction Energy
© 1997
Boris Veytsman
and Michael Kotelyanskii
Thu Sep 18 22:50:29 EDT 1997
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() when
when ![]() .
.![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() . This is collision. Low density gas--not many
collisions! Take a volume V, where collisions are rare. It means
neglecting products of f-functions.
. This is collision. Low density gas--not many
collisions! Take a volume V, where collisions are rare. It means
neglecting products of f-functions.
![]()
![]()
![]()
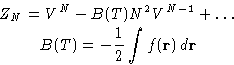
![]()
![]() , we obtained:
, we obtained:
![]()
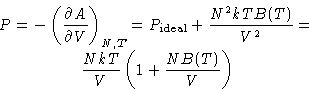
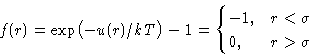
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()